Welcome to the world of Machine Learning (ML)! Are you ready to explore how computers can learn from data and make smart decisions? Let’s dive in—this guide will answer key questions and give you the foundation to start building your own AI projects.
1. What is Machine Learning?
Ever wonder how Netflix knows what to recommend or how your email filters spam? That’s Machine Learning! It looks at data, finds patterns, makes predictions, and gets smarter over time based on your actions.
Netflix looks at what you watch, your ratings, and other users’ habits to suggest shows you’ll like. Similarly, email filters analyze patterns in messages, like subject lines and content, to detect spam. In short, ML learns from data, finds patterns, makes predictions, and gets smarter over time.
Machine Learning (ML) is a core part of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It allows computers to learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed for every task. By analyzing large amounts of information, ML systems can recognize patterns, make predictions, and take intelligent actions.
For example Similar to above Netflix and email filter:
– A music app learns your listening habits and suggests new songs you might like.
– An e-commerce site predicts which products you’re likely to buy next.
– Self-driving cars detect pedestrians, traffic signs, and road conditions to make safe driving decisions.
In short, Machine Learning lets computers learn from data, spot patterns, and make smart decisions on their own—turning raw information into useful insights you can apply in the real world. The following paragraphs provide more details on why you should learn Machine Learning, how it works, and the key concepts that will help you build practical AI skills.
Question to think about: What everyday tools do you use that might already be using ML? [ Go to Top ]
2. Why You Should Learn Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is one of the fastest-growing skills in today’s tech-driven world. Companies across industries—like finance, healthcare, marketing, education, and e-commerce—are actively looking for professionals who can analyze data, build predictive models, and create intelligent systems.
By learning ML, you can: Solve real-world problems by building solutions like recommendation engines, fraud detection systems, or intelligent automation that make a tangible impact. such solutions use Predictive models (e.g., forecasting sales or stock trends), Recommendation systems (e.g., Netflix or Amazon suggestions) and Intelligent automation (e.g., smart assistants or automated workflows).
In addition, learning Machine Learning will boost your career opportunities. ML skills are in high demand, opening doors to roles in AI, data science, analytics, and software development, and giving you a competitive edge in today’s tech-driven world. In addition, learning Machine Learning will boost your career opportunities, help you stay ahead in the AI revolution, and enhance productivity and innovation. ML skills are in high demand, opening doors to roles in AI, data science, analytics, and software development, while also enabling you to automate tasks, gain insights from data, and create smarter solutions.
Think about it: Whether you want to improve your current job, start a tech career, or create your own AI-powered solutions, mastering ML gives you the tools to turn data into action.
To kickstart your Machine Learning journey, it’s important to understand the core concepts that form the foundation of ML. The following section will cover the main types of learning, data and model basics, and important techniques to help you build effective and accurate ML models.
Question to think about: How could you use ML in your work, study, or hobbies? [ Go to Top ]
3. Key Concepts You Need to Know
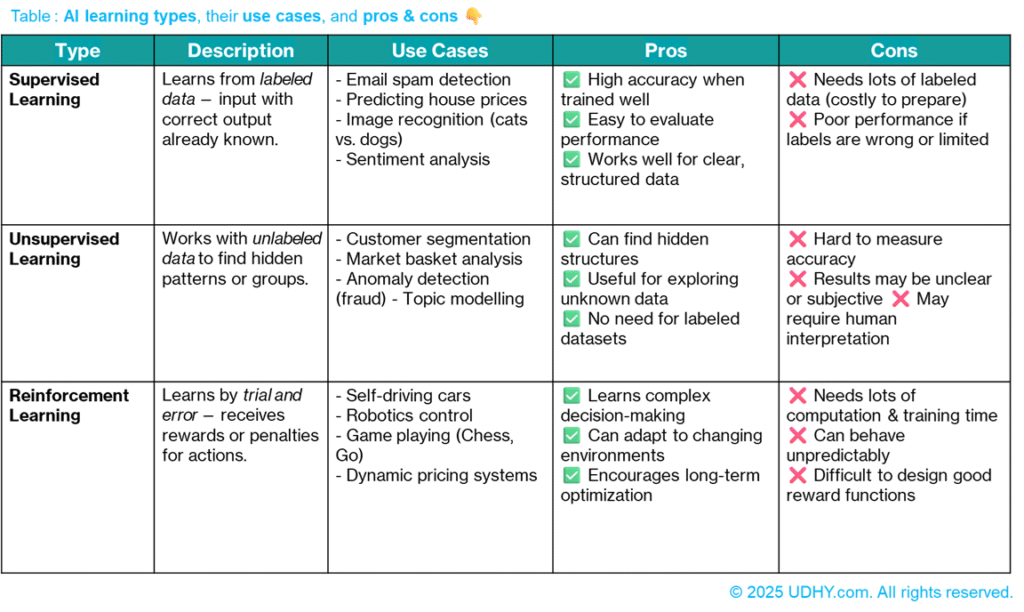
Machine Learning can be divided into three main types, depending on how the system learns from data, as shown in the table :
3.1. Types of Learning
* Supervised Learning: Trains a model using labeled data (inputs with correct outputs) to predict new results. It’s accurate and reliable but needs a large amount of labeled data, which can be time-consuming and costly — like a student learning from an answer key.
* Unsupervised Learning: Works with unlabeled data to find hidden patterns or groups, but the results can be harder to interpret and evaluate.
* Reinforcement Learning: Learns through trial and error, improving based on rewards or penalties. It’s great for robots and games but requires significant time and computing power to train.
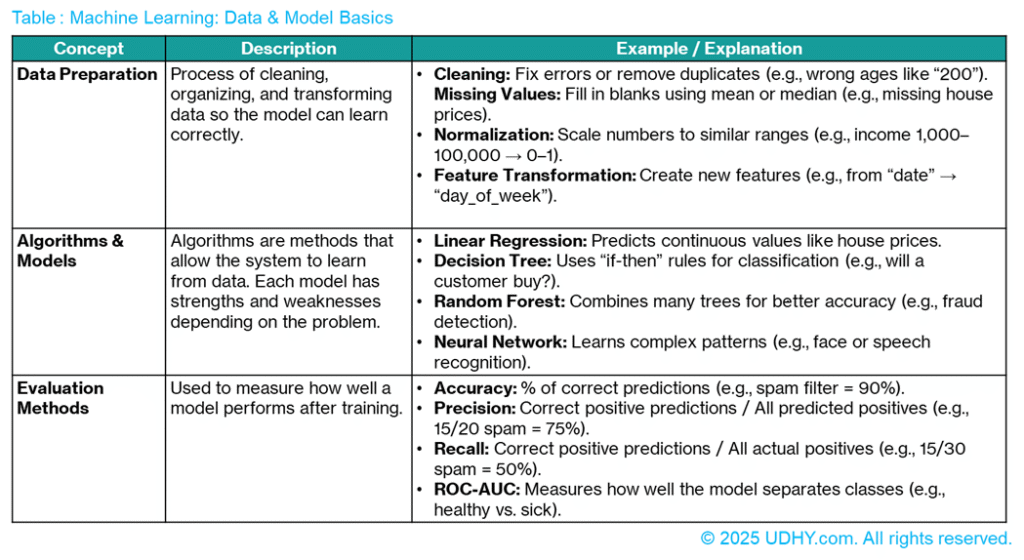
3.2. Data & Model Basics
In Machine Learning, data is the foundation — it’s what helps computers learn and make decisions. The quality and preparation of data directly affect how well your model performs. Table Machine Learning: Data & Model Basics table helps you clearly understand each concept in Machine Learning (ML) 👇
* Data Preparation: Clean data, handle missing values, normalize, and transform features for better learning.
* Algorithms & Models: From linear regression to decision trees to neural networks, each has strengths and trade-offs.
* Evaluation Methods: Use metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and ROC-AUC to measure performance.
3.3. Overfitting & Generalization Models can sometimes learn the training data too well, including noise, which makes them perform poorly on new data. Techniques like cross-validation, regularization, and simplifying models help avoid this.
Question to think about: Why do you think it’s important for a model to perform well on new, unseen data? [ Go to Top ]
4. Common Algorithms Simplified
Machine Learning uses different types of algorithms to help computers learn from data and make predictions or decisions. Each algorithm has its own strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases depending on the problem. Below are some of the most common and important algorithms used in real-world applications.
4.1 Linear & Logistic Regression: Great starting point for prediction problems. The Linear and Logistic Regression are the simplest and most widely used starting points for prediction tasks. Linear regression predicts continuous values such as house prices or sales numbers, while logistic regression predicts categorical outcomes such as whether an email is spam or not. These methods are easy to understand, train quickly, and work best when the relationship between inputs and outputs is relatively simple.
4.2 Decision Trees & Random Forests: Easy to interpret; useful for classification and regression. The Decision Trees and Random Forests make predictions by asking a series of “if–then” questions. A decision tree is easy to interpret and visualize, while a random forest combines many trees to increase accuracy and reduce errors. They are commonly used in areas such as loan approval, risk analysis, or predicting customer churn. However, single decision trees can overfit the data if not properly managed.
4.3 K-Means Clustering: Groups data points without labeled outputs. The K-Means Clustering is an unsupervised learning algorithm that groups data points into clusters based on similarity. It is often used to segment customers into different groups or to organize data without predefined labels. This method is great for finding hidden patterns in large datasets, though it requires you to choose the number of clusters (K) in advance.
4.4 Neural Networks: The foundation of deep learning; useful for images, speech, and complex data. The Neural Networks form the foundation of deep learning and are inspired by how the human brain works. They consist of layers of “neurons” that process information and learn complex relationships in data. Neural networks are extremely powerful and are used in image recognition, speech processing, and autonomous driving. However, they require large amounts of data and computing power to perform well.
Question to think about: Can you think of a problem you could solve with one of these algorithms? [ Go to Top ]
5. Real-World Applications
Machine Learning is everywhere! Examples include:
* Healthcare: Disease diagnosis, patient outcome prediction, medical image analysis
* Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading
* Retail & E-commerce: Recommendation systems, customer segmentation
* Transport & Smart Cities: Predictive maintenance, traffic management, autonomous systems
Question to think about: Which real-world application excites you the most, and why?[ Go to Top ]
6. How to Get Started
Ready to dive in? Follow these simple steps:
6.1 Learn the Basics
Start by gaining comfort with the core skills needed for ML:
* Python: Most ML libraries and tools use Python, so practice coding and working with data structures.
* Statistics & Math: Understand concepts like mean, variance, probability, and distributions—they help you interpret data and evaluate models.
* Data Handling: Learn to clean, organize, and manipulate datasets using tools like pandas and NumPy.
6.2 Try a Project
Hands-on practice is key. Start with a small, simple dataset to build your first ML project:
* Example: Predicting house prices, classifying emails as spam or not, or sorting fruits by features.
* Focus on building either a classification or regression model depending on your problem.
* Step-by-step practice helps you understand data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation.
6.3 Use Tools & Libraries
Explore popular ML tools and libraries to simplify your workflow:
* scikit-learn: Perfect for beginners; easy to implement classification, regression, and clustering.
* TensorFlow & PyTorch: More advanced; used for deep learning and neural networks.
* Visualization tools: Matplotlib, Seaborn, or Plotly to understand and present data effectively.
6.4 Practice Regularly
* ML is learned by doing: experiment, iterate, and test different approaches.
* Challenge yourself with small competitions or datasets, like those on Kaggle, to improve problem-solving skills.
* Practice helps you understand model limitations, tweak hyperparameters, and improve predictions.
6.5 Join the Community
* Share your projects and ideas with others to receive feedback and learn best practices.
* Engage in forums like Kaggle, Stack Overflow, or Reddit ML communities.
* Collaboration keeps you motivated and helps you stay updated on new techniques and trends in ML.
Tip: Start small, be consistent, and gradually take on more complex projects. Learning ML is a journey, and each step builds the foundation for advanced AI skills. [ Go to Top ]
Join & start your AI & Robotics journey with UDHY.
Enter your email address to register to our newsletter subscription delivered on regular basis!
